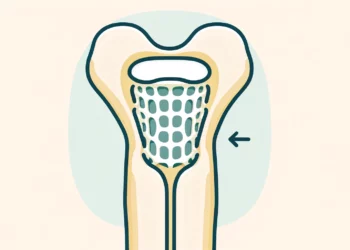
Bone implants are poised to receive an upgrade, as researchers from the University of British Columbia and McMaster University have developed a new foam-like substance for this purpose.

Image credits Clare Kiernan / UBC.
Most bone implants today are made of hard ceramics. They’re hardy enough for the job, but the material is also very brittle, making it hard to work with. It’s also very tricky getting these implants to conform to the shape of the fractures or holes in the damaged bone — which often leads to the implant failing.
Sponge it
“We created this cellulose nanocrystal aerogel as a more effective alternative to these synthetic materials,” said study author Daniel Osorio, a Ph.D. student in chemical engineering at McMaster.
The team developed a foam-like substance (aerogel) that can be injected into damaged bones to provide scaffolding for the growth of new tissue. It’s formed of nanocrystals obtained from treated plant cellulose which can link up to form a strong but lightweight ‘sponge’ which is strong but also capable to expand or compress in order to fill out a cavity.
In order to test their aerogel, the team worked with two groups of rats. The first received the aerogel implants while the second (control group) received none. Over a three-week period, the first group saw 33% more bone growth and 50% more bone growth by the 12-week mark compared to the control group.
The team says these results show that cellulose nanocrystal aerogels are a viable, even preferable, medium to support bone growth. The implants will break down over time into non-toxic components in the body as bones heal, they add, limiting the need for further invasive procedures and treatments. All in all, even if the material doesn’t remove traditional implants, it is bound to find use as a supportive or novel treatment avenue in lieu of traditional materials.
“We can see this aerogel being used for a number of applications including dental implants and spinal and joint replacement surgeries,” said Grandfield. “And it will be economical because the raw material, the nanocellulose, is already being produced in commercial quantities.”
That being said, we’re still a ways away until the aerogel is ready for use in operating rooms across the world.
“This summer, we will study the mechanisms between the bone and implant that lead to bone growth,” said Grandfield. “We’ll also look at how the implant degrades using advanced microscopes. After that, more biological testing will be required before it is ready for clinical trials.”
The paper “Cross-linked cellulose nanocrystal aerogels as viable bone tissue scaffolds” has been published in the journal Acta Biomaterialia.