NASA’s Mars rover, the Perseverance, was aptly named. After delaying its launch (July 17) by three days, the agency has now rescheduled it for July 22 due to “a contamination concern”.

The agency initially delayed the launch due to issues with ground equipment, namely a faulty crane. As this was being fixed, engineers also ran into trouble as they were mounting the Atlas V rocket’s nosecone to its body (creating the space that transports the rover). Due to this, Perserverence’s launch was rescheduled for July 22, NASA said on Wednesday.
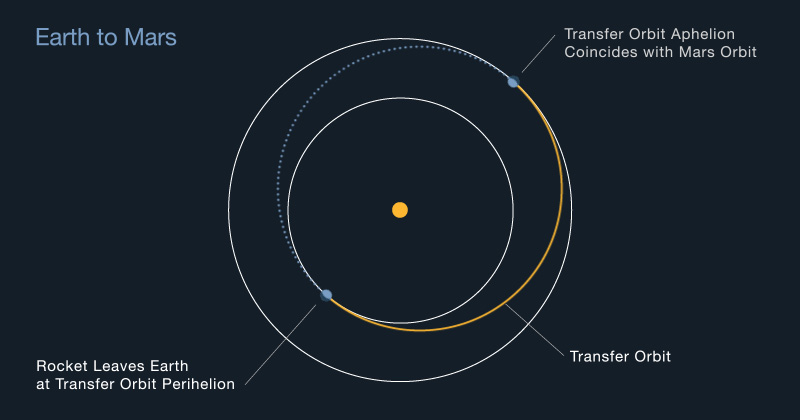
Earth and Mars don’t stay at a constant distance all the time. They move around the Sun at different speeds and on different orbits. The launch window to Mars, the span of time when its closest to Earth, is open until Aug. 11. So despite the delay, NASA isn’t worried about not being ready on time.
“NASA and United Launch Alliance [who built the rocket] are now targeting Wednesday, July 22, for launch of the Mars 2020 mission due to a processing delay encountered during encapsulation activities of the spacecraft,” the agency writes.
“Additional time was needed to resolve a contamination concern in the ground support lines in NASA’s Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF).”
NASA adds that “the spacecraft and vehicle remain healthy”, and successfully performed a refueling test on Monday.
Launch director Omar Baez said in a news conference that “[they] have plenty of window or runway ahead of us and we’re not worried about it”. He said that further setbacks from “not-so-perfect days” are probable but that the team will still be ready for launch. It may even be possible to extend the launch window to Aug. 15, Baez added.
Perseverance is scheduled to land on Mars on Feb. 18, 2021. Its target is the Jezero Crater, a 49 km (30.5 mi) wide crater thought to have contained liquid water at some point in the past. There, it will look for signs of ancient life and take samples that will be retrieved on a later mission. One of its most important tasks is to test MOXIE — a system that creates oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, which is rich in carbon dioxide.
Perseverance’s design is largely based on the Curiosity rover, the last rover to land on Mars. It’s heavier, carries fewer instruments, but is also equipped with a nuclear power source — which should keep the rover running for a long time.

Image credits NASA / JPL-Caltech.
Perseverance is the first rover to also bring along a colleague: Ingenuity, the first helicopter sent to space. The tiny flier will initially make three test runs in the Martian atmosphere, though it could make more if everything goes well.
Of course, this all hinges on NASA making the launch window. If they don’t, we will have to wait for another 26 months for the two planets to properly align again.






