The development of the standard cosmological model (sometimes called ΛCDM or the Lambda-CDM) is the simplest model that provides a reasonable explanation of what we see in the universe. The was based on a set of equations proposed by a Russian physicist named Alexander Friedmann. On June 29th, the Friedmann equations turned 100.

Olbers paradox
Imagine you’re trying to answer a preschooler’s question about the universe: “how many stars exist in the universe?”. You’re not sure what to answer. We don’t really know if the universe is infinite or not, so the answer is somewhere between “a bajillion” and “an infinite number”. But preschoolers are relentless, so the little one asks once more: “If there are so many stars, then why is the sky dark at night?”
That question may sound silly, but it’s actually so profound there’s actually a name for it. It’s called Olbers’ paradox, named after the German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers. If you assume there are infinite light sources in the universe, or even just a lot of stars, then how come what we see is mostly dark?

Olbers proposed that there’s a medium that prevents the light emitted by stars from reaching farther than a specific distance. We know that is not true now.
Other attempts to solve the paradox include the finite life of a star, which means that stars are appearing and disappearing at a constant rate, but that alone wouldn’t be enough to account for the number of stars distributed in a static universe. Astronomers have also argued that stars aren’t distributed uniformly across the universe, so you can have some portions of the sky riddled with stars, while other are devoid of almost any stars.
Still, that doesn’t really address the problem and it’s still not a satisfactory solution. The solution comes from the universe itself, which seems to be expanding at such a speed that faraway stars’ brightness is suppressed.
Friedmann equations
Friedmann followed general relativity equations to try to write general equations which could describe the dynamics of the universe. Back then, there were two known physical models that attempted to describe the universe. One universe was described by Einstein and the other by Dutch astronomer Willem de Sitter.
Einstein’s solution consisted of a cylindrical static universe — to overcome the mathematical challenges raised by this model, Einstein used a trick: he added a number, lambda, that basically made the universe static. Meanwhile, de Sitter’s universe was spherical, but also static. Friedmann tried to get those two solutions from a general description.
But as Friedmann worked through his general equations, he realized that there’s no real need for a static universe, as was originally thought. His model worked just fine with a universe that expanded or contracted.
If the universe were to contract, that wouldn’t help explain Olbers’ Paradox — things would be moving closer to us, so we’d see them even brighter. But if it were expanding, then we could be onto something.
Cosmology and evidence
In 1929, Edwin Hubble, an astronomer at Caltech found evidence that the universe was indeed expanding. But Friedmann was working in 1922, and at first, his publication wasn’t accepted by the scientific community.
Friedmann actually studied physics applied to meteorology. His knowledge was used during World War I as an air force ballistics instructor. During the 1920s, he focused on turbulence and aerodynamics research and at the same time he was working on general relativity.
When people didn’t like the idea of a non-static universe. Friedmann had to write to Einstein himself to convince him the equations did make sense but slowly, his idea started to catch on.
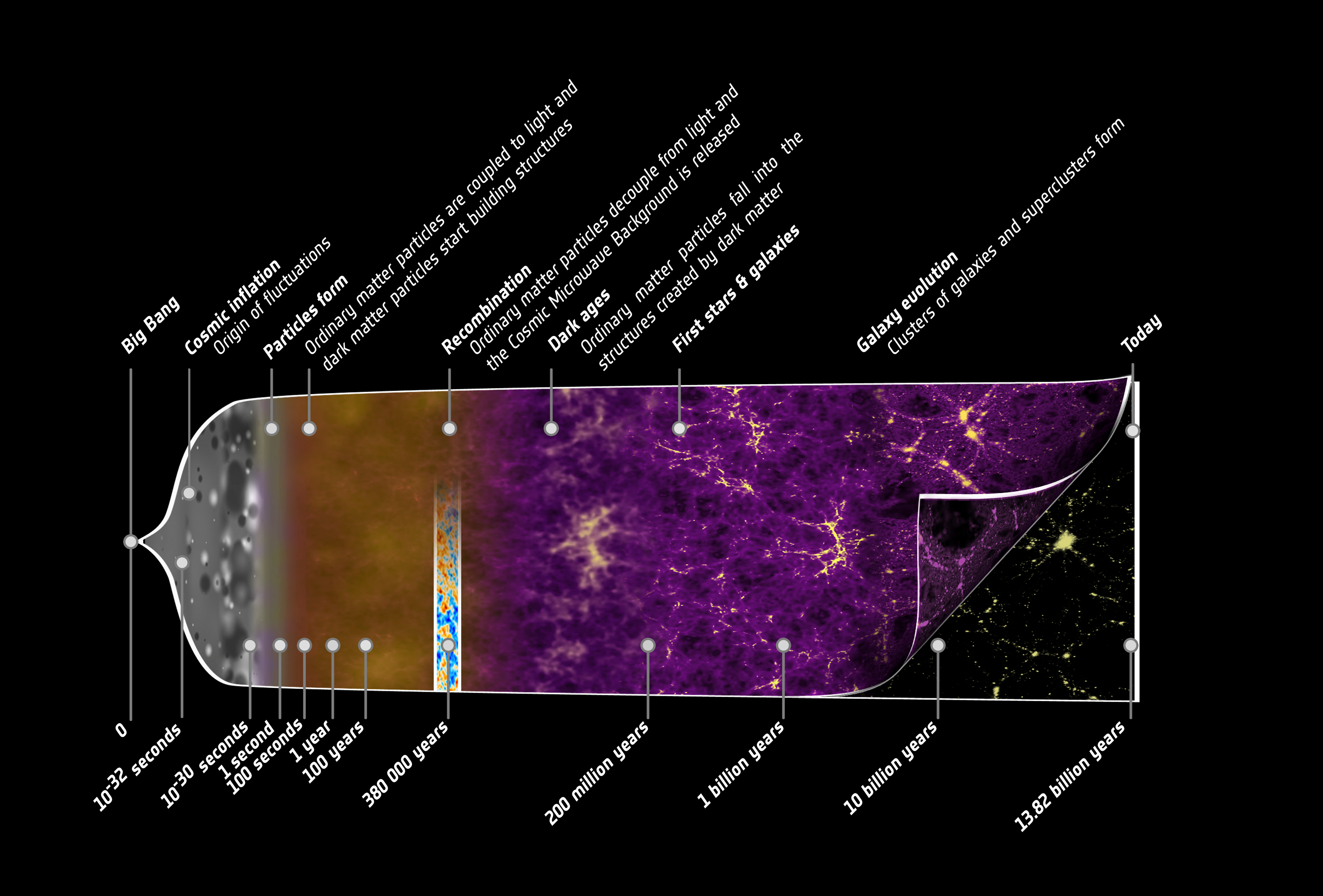
The result of Friedmann’s equations is what we now call the standard model of cosmology, or the ΛCDM model. Each letter in the acronym represents the things that we believe account for most of the universe’s composition. Λ is for the lambda Einstein added to make the universe static — but, ironically, the number represents a factor that accounts for the universal expansion, which astronomers now think could be linked to dark energy. CDM stands for cold dark matter, another mysterious ingredient we still don’t really understand.
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) signal contains the best observations of the universe so far. Modern satellite results agree with the ΛCDM model, as do other observations such as supernovae light curves.
However, there is tension between the CMB and supernovae results, called the Hubble tension. Different probes seem to show different results of the Hubble constant (expansion rate). This problem is presently being tackled by considering better observations or possibly making a change in the standard model, but nothing conclusive yet. Simply put, while the Friedmann equations still stand in general principle, the nuts and bolts of how the universe is expanding and what exactly is triggering this change is still unclear.
Friedmann’s results in cosmology shaped the theory that we describe how the universe started very dense and expanded to the one we see today. All the high-precision telescopes and various mission results evoke Friedmann’s equations in an attempt to understand the cosmos.






