The ECMWF’s Copernicus reanalysis had already stated the year of 2020 as the warmest on the record. Now, other five independent analyses surveyed by World Meteorological Organization (WMO) show that it was at least one of the three warmest years. The teams are: United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), NASA’s Goddard Institute for Space Studies (NASA GISS), and the United Kingdom’s Met Office Hadley Centre and the University of East Anglia’s Climatic Research Unit (HadCRUT) and another reanalysis from Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA).
WMO has shown five of its data sets indicating that 2020 was a hot year, with a global average temperature of 14.9°C. This is 1.2°C above the average temperature before industrial activity.
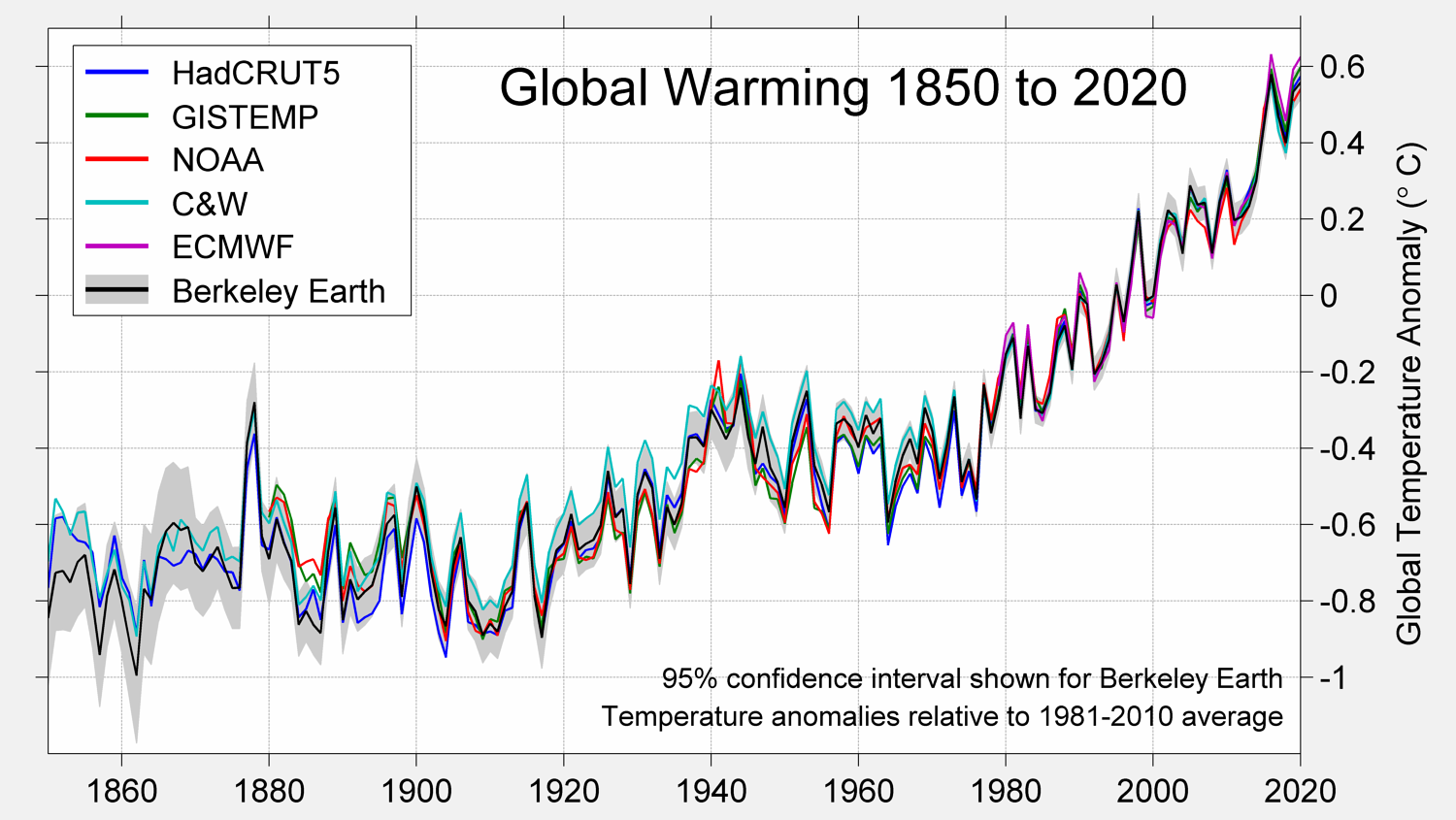
The centers that analyzed the data consider all sorts of instrumental data, buoys in the sea, stations, aircraft, and satellites. This is usually similar to all approaches, what differs is the way they interpolate the data.
Interpolation means a way of estimating data for a place that did not have a real measurement. Just like superhero movies, when the hero wants to find the source of a villainous activity. Researchers sometimes use the word “triangulate”, which is a form of interpolation. This explains why some researchers report slightly different results. For instance, NASA interpolates data considering the poles, NOAA doesn’t and other centers also vary their methodology, so the average temperature will differ.
NASA agrees with ECMWF in that 2020 is tied with 2016 for ignoble honor of the warmest year on record. NOAA and HadCRUT say it’s the second warmest and JMA says it’s the third warmest. What matters is that it was a very warm year despite the formation La Niña, which tends to reduce the average. The 2016 had the help of El Niño to increase the temperature, which means 2020 was far too warm.
The sixth dataset is from Berkeley Earth, an independent, non-governmental group that gathers data to study climate change. The founder, Richard A. Muller, started the project because he believed some skeptics pointed problems in the way the traditional centers, such as NASA, delivered their results. Spoiler alert: after the first analysis they concluded the data didn’t differ so much from everyone else.
Berkeley Earth concluded that 2020 was the second warmest year since 1850, differing only by 0.022°C. For 45 countries, 2020 was the warmest year ever, especially for European countries. This is because land warms faster than the ocean and the Northern Hemisphere has more land cover. Russia warmed the most, by a staggering 4°C above the pre-industrial era.
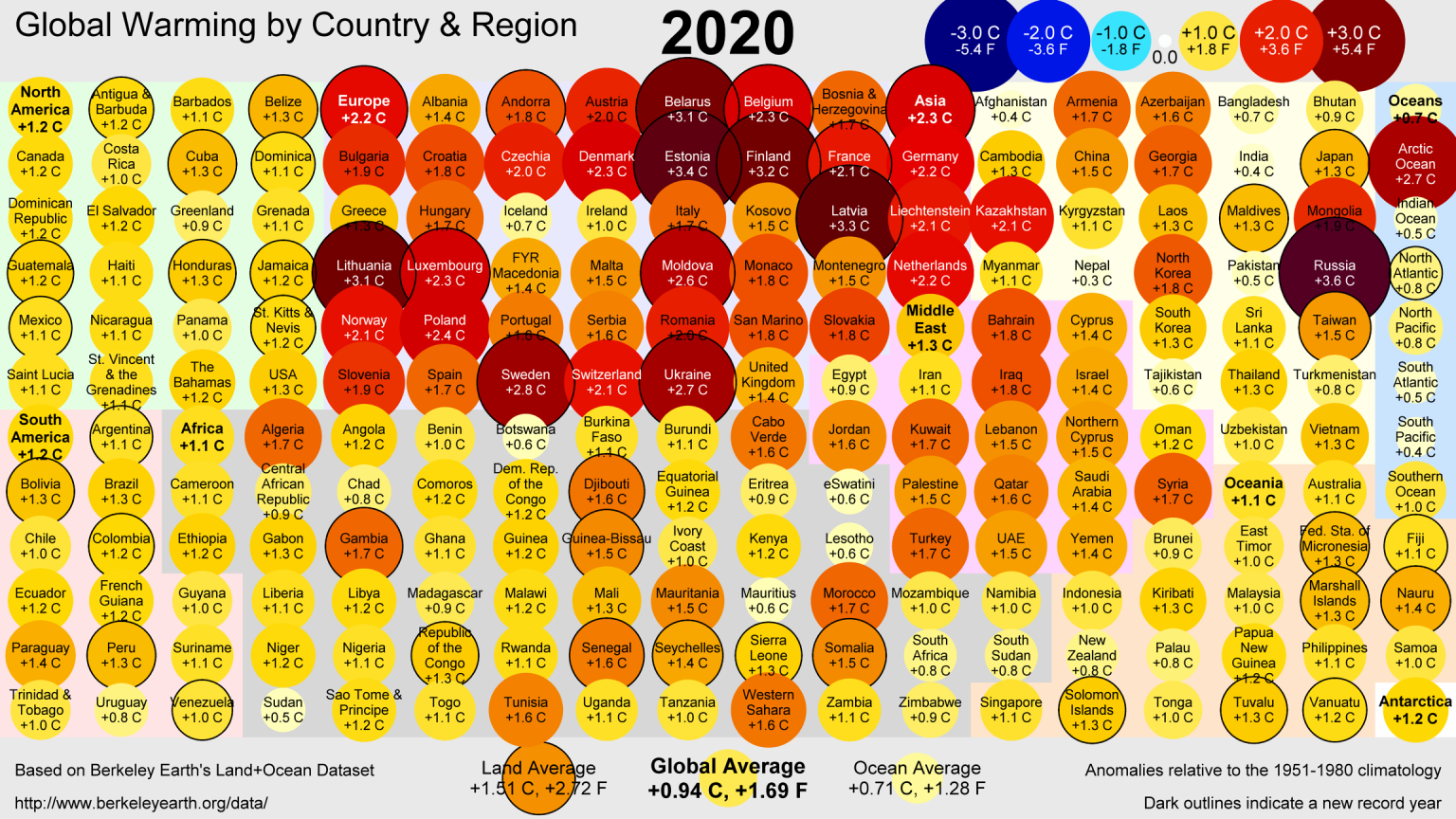
The year 2021 may not be as hot as 2020 due to the continuation of the La Niña event. Scientists estimate that it could come in fifth place in the heat race. It is important to note that Berkeley Earth’s estimate is just a minor perturbation in the trend. This doesn’t mean an end to global warming.
Unfortunately, Berkeley showed the trending of the temperature curve and it looks terrible. If we continue with the pace we are now, by 2037 the world could be 1.5°C above the 1850-1900 trend. Paris Agreement established the 2°C or less threshold in order to avoid an even worse climate crisis.
Was this helpful?



