- 🐭 Mice demonstrated self-recognition-like behavior in mirror tests, but this ability is more nuanced than in other creatures.
- 🧠 Specific neurons in mice’s hippocampus link self-perception to social experiences, suggesting broader implications for understanding self-awareness.
- 🧪 The study suggests tactile stimuli are crucial for mice self-recognition, differing from big-brained species like chimpanzees and humans.
Researchers found mice exhibit behavior akin to self-recognition, a phenomenon previously thought to be limited to humans and certain larger-brained mammals. This discovery offers a new perspective on understanding the neural mechanisms behind self-awareness.
A mirror to the self
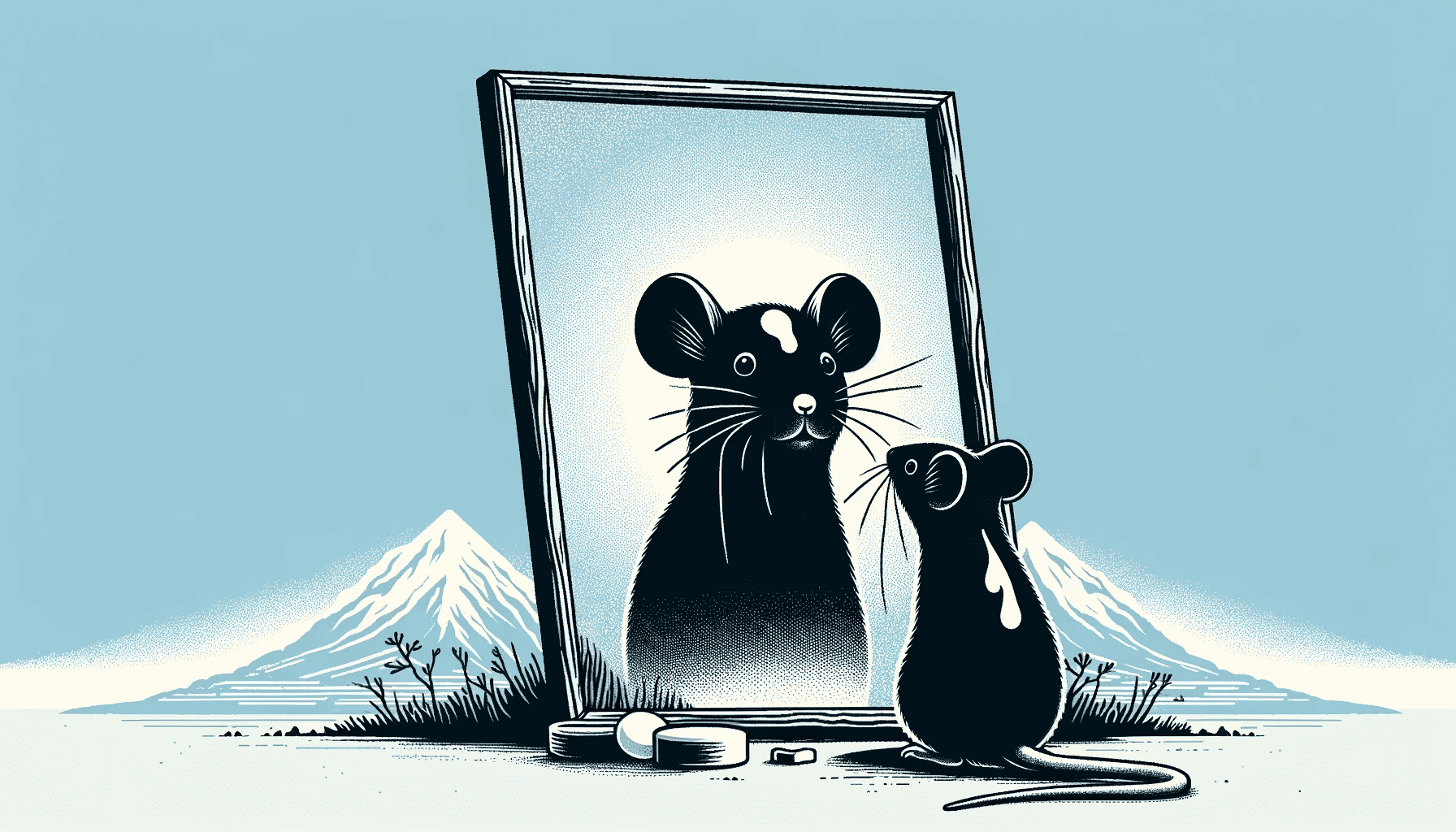
The experiment revolved around the classic mirror test, traditionally used to assess self-awareness in different species. The mirror test, also known as the Mirror Self-Recognition Test (MSR), is very simple: researchers place a mark on an animal in a location that it can’t see without a mirror. Then, they observe how the animal reacts to its reflection. If the animal uses the mirror to investigate and possibly try to remove the mark, it’s considered evidence of self-recognition — a fundamental aspect of self-awareness.
Mice, accustomed to mirrors and sharing a habitat with similarly black-furred mice, were marked with a noticeable white ink spot on their foreheads. Remarkably, these mice demonstrated increased grooming behavior in front of mirrors, presumably attempting to remove the unfamiliar white spot.
This behavior contrasts starkly with mice that were either not used to mirrors or had less conspicuous markings. The absence of increased grooming in these cases hints at a nuanced understanding of self-image in mice, contingent on certain sensory and social conditions.
“The mice required significant external sensory cues to pass the mirror test — we have to put a lot of ink on their heads, and then the tactile stimulus coming from the ink somehow enables the animal to detect the ink on their heads via a mirror reflection,” says first author Jun Yokose of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center.
“Chimps and humans don’t need any of that extra sensory stimulus.”
Delving deeper, the team, led by neuroscientist Takashi Kitamura of the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, identified specific neurons in the hippocampus that played a pivotal role in this self-recognition-like behavior. The activation of these neurons not only occurred when the mice viewed themselves in mirrors but also when observing other mice of the same species variant (and therefore of the same appearance), suggesting a link between social experience and self-perception.
“To form episodic memory, for example, of events in our daily life, brains form and store information about where, what, when, and who, and the most important component is self-information or status,” says Kitamura.
“Researchers usually examine how the brain encodes or recognizes others, but the self-information aspect is unclear.”
Interestingly, socially isolated mice or those raised with differently colored mice showed no signs of such neural activity that encodes a visual self-image. This finding aligns with previous studies in chimpanzees and monkeys, which suggested social experience and social interactions are crucial in developing self-recognition abilities.
Beyond the reflection
While the study reveals that mice can detect changes in their appearance, it stops short of confirming self-awareness as understood in humans or primates. The researchers note that the tactile sensation from the ink was crucial for the mice to notice the change, a requirement not needed in higher-intelligence species like chimpanzees or humans.
Other animals that have past the mirror test include Asian elephants, dolphins, and orcas, as well as roosters and even fish.
In future research, the scientists want to delve deeper into the roles of visual and tactile stimuli and explore other brain regions involved in this complex process. This inquiry would pave the way for a better understanding of the neural circuitry underpinning self-recognition and its development across different species.
The findings appeared in the journal Neuron.






