A set of fossils collected 35 years ago belonged to the oldest-known scorpion species to date, a new study reports.

Image credits Andrew Wendruff et al., (2020), Nature.
The scorpion lived around 437 million years ago and was surprisingly versatile, having the ability to breathe both on land and underwater, the team explains. This fossil helps us make better sense not only of the scorpions’ evolutionary path, but also of how animals transitioned from an aquatic lifestyle to living on dry land.
The first scorpion
“We’re looking at the oldest known scorpion — the oldest known member of the arachnid lineage, which has been one of the most successful land-going creatures in all of Earth history,” said Loren Babcock, an author of the study and a professor of earth sciences at The Ohio State University.
In a new study describing the fossils, researchers named the new species Parioscorpio venator, meaning “parent scorpion hunter”. The fossil was first unearthed in 1985 in Wisconsin at a site that was once a shallow pool on the base of an island cliff face. For 30 years, it was kept in a museum at the University of Wisconsin until Andrew Wendruff, paper co-author and now an adjunct professor at Otterbein University in Westerville, decided to examine it in detail.
This scorpion is about 2.5 centimeters long, similar to many wild scorpions today. Wendruff looked at the fossil under a microscope, taking high-resolution photographs of it from different angles. This process helped highlight bits of the animal’s internal organs, allowing Wendruff to identify its venom appendages and the remains of its respiratory and circulatory systems.
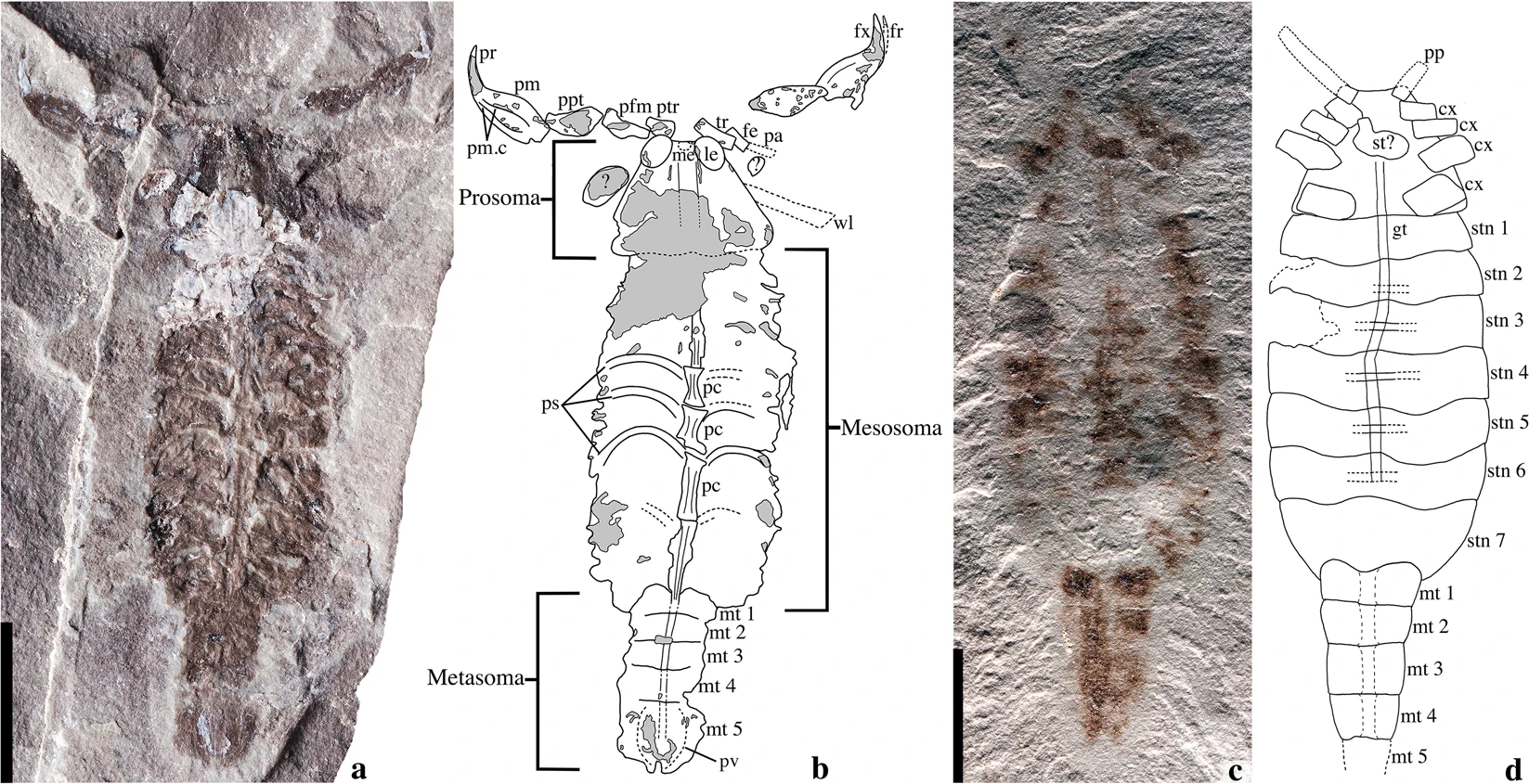
Image credits Andrew Wendruff et al., (2020), Nature.
This system is almost identical to those of modern scorpions (which are exclusively land-living) but function more closely to those of horseshoe crabs (which are predominantly aquatic but can breathe on dry land for short periods of time).
The discovery provides new information about how animals transitioned from living in the sea to living entirely on land: The scorpion’s respiratory and circulatory systems are almost identical to those of our modern-day scorpions — which spend their lives exclusively on land — but operate similarly to those of a horseshoe crab, which lives mostly in the water, but which is capable of forays onto land for short periods of time.
The oldest-known scorpion prior to this study had been found in Scotland and dated to about 434 million years ago — it was one of the first animals (that we know of) to live fully on land. This fossil, found in Wisconsin in the Brandon Bridge Formation, is between 1 million and 3 million years older, the authors explain. They were likely alive between 436.5 and 437.5 million years ago, during the late Paleozoic era.
“What is of even greater significance is that we’ve identified a mechanism by which animals made that critical transition from a marine habitat to a terrestrial habitat. It provides a model for other kinds of animals that have made that transition including, potentially, vertebrate animals. It’s a groundbreaking discovery.”
The paper “A Silurian ancestral scorpion with fossilised internal anatomy illustrating a pathway to arachnid terrestrialisation” has been published in the journal Scientific Reports.









