Three different ways to breathe:
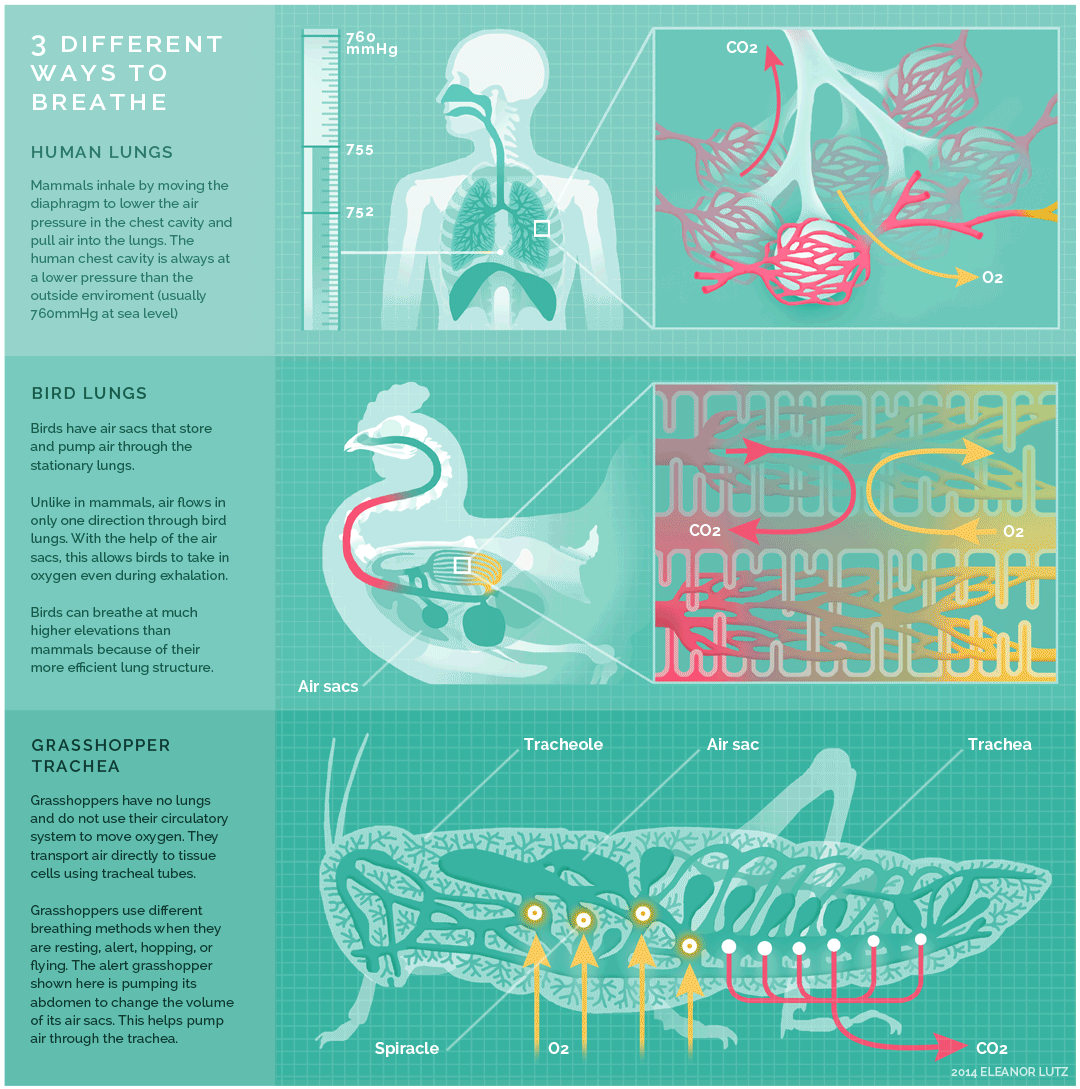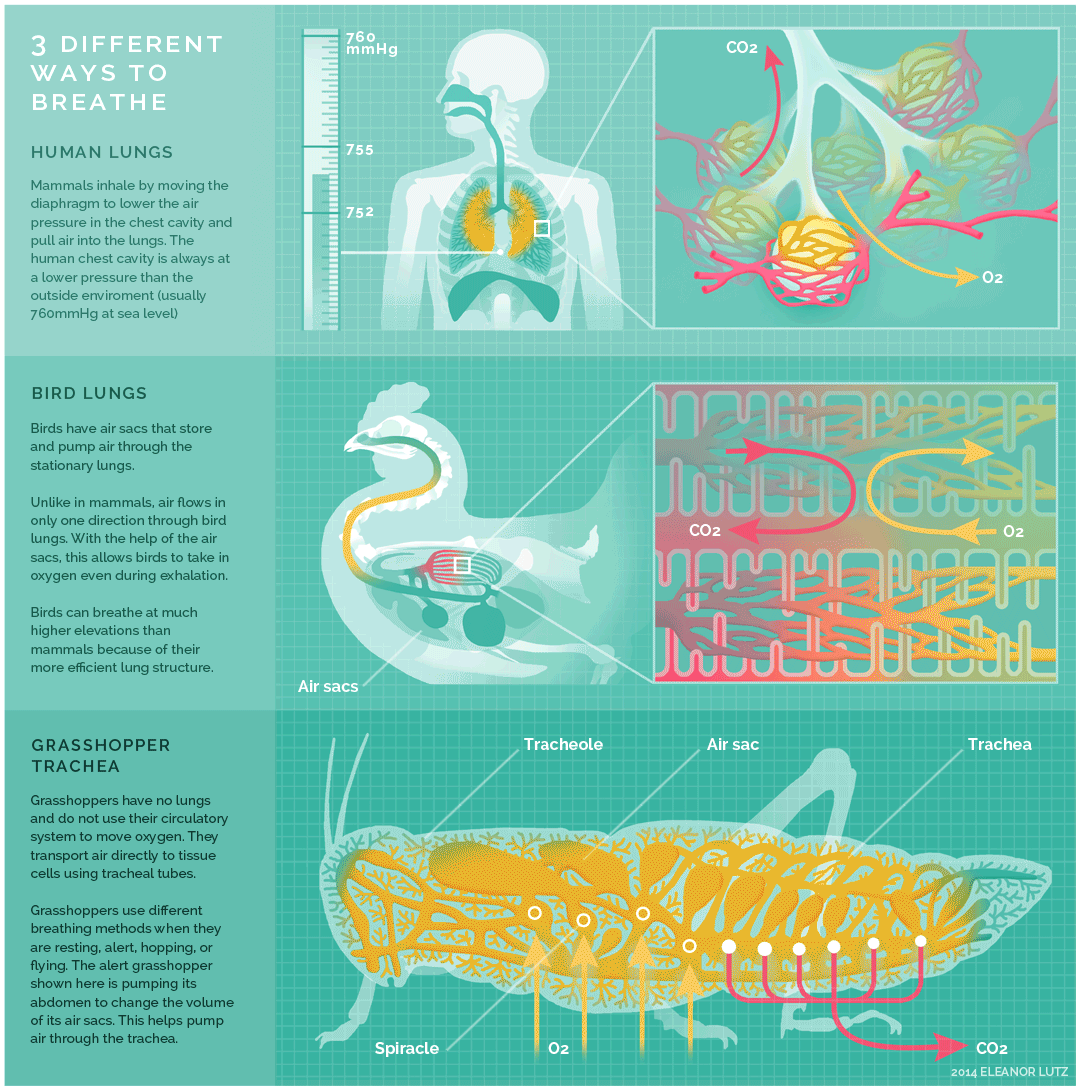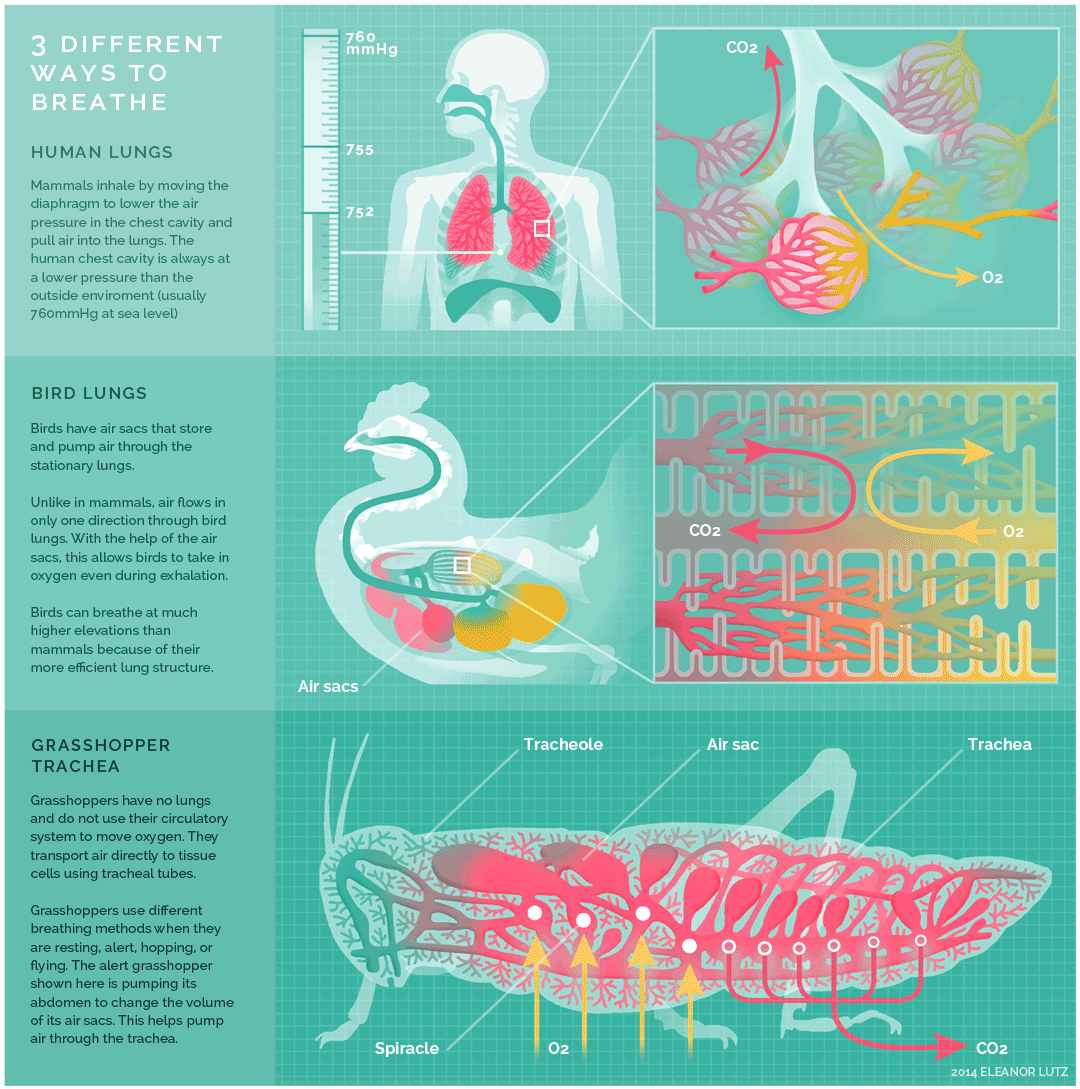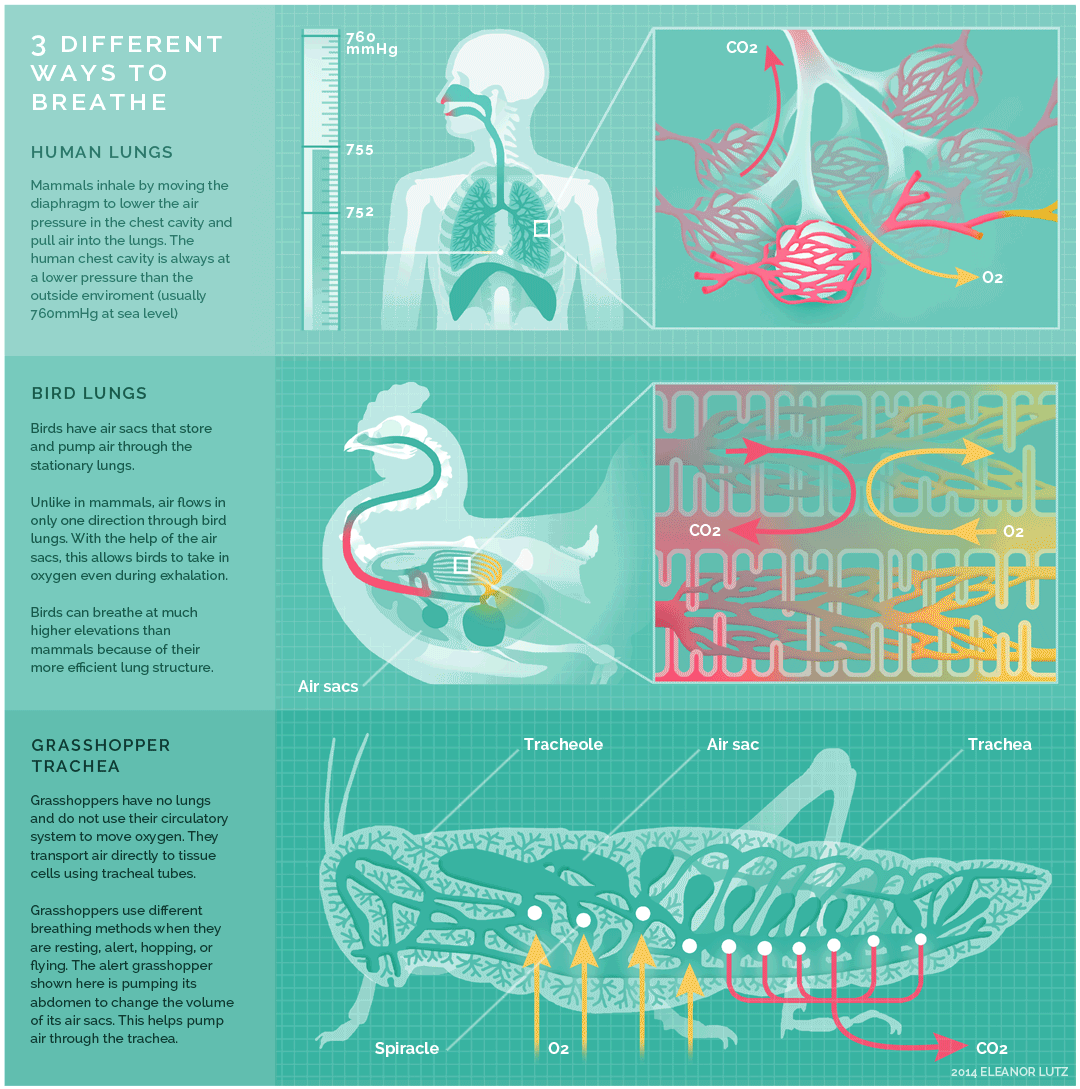
Mammals, birds and insects breathe in different ways, as exemplified above. Humans, as mammals, inhale by moving the diaphragm to lower the air pressure in the chest cavity and pull air into the lungs. The human chest cavity is always at a lower pressure than the outside environment.
Birds on the other hand, have air sacs that reach into the bones, and have no diaphragm, respiratory infections can spread to the abdominal cavity and bones. Bird lungs do not expand or contract like the lungs of mammals. Unlike in mammals, air flows only in one direction and this allows birds to take in oxygen even as they exhale.
Insects have no lungs. Instead of lungs, insects breathe with a network of tiny tubes called tracheae. Air enters the tubes through a row of holes along an insect’s abdomen. The air then diffuses down the blind-ended tracheae. Since the biggest bugs have the longest tracheae, they should need the most oxygen to be able to breathe. Grasshoppers use different breathing methods when they are resting, alert, hopping or flying. Here, an alert grasshopper is depicted.
Credits: Eleanor Lutz









